Researchers Find New Organ
Researchers have identified a previously unknown feature of human anatomy with implications for the function of all organs, most tissues, and the mechanisms of most major diseases.
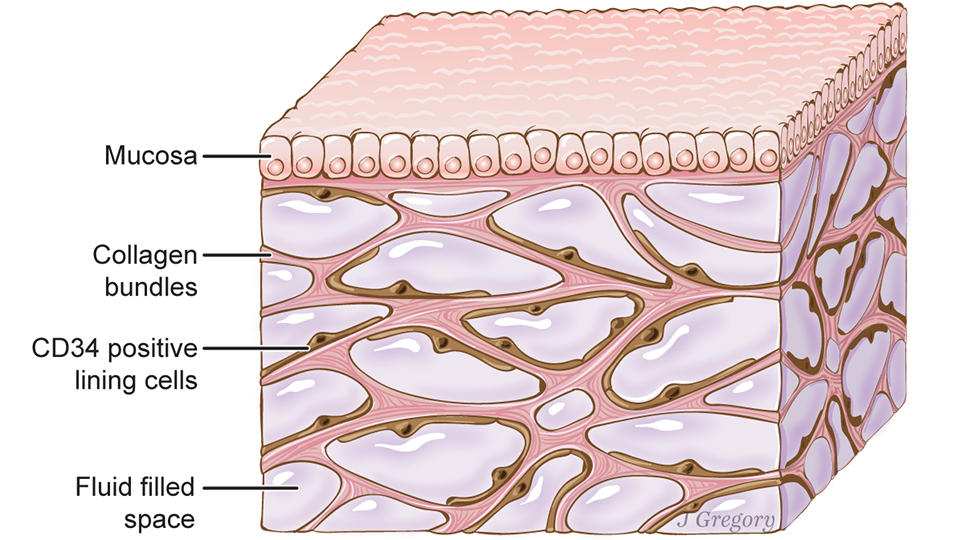
Published March 27 in Scientific Reports, a new study co-led by an NYU School of Medicine pathologist reveals that layers of the body long thought to be dense, connective tissues—below the skin’s surface, lining the digestive tract, lungs, and urinary systems, and surrounding arteries, veins, and the fascia between muscles—are instead interconnected, fluid-filled compartments.
This series of spaces, supported by a meshwork of strong (collagen) and flexible (elastin) connective tissue proteins, may act like shock absorbers that keep tissues from tearing as organs, muscles, and vessels squeeze, pump, and pulse as part of daily function.
Importantly, the finding that this layer is a highway of moving fluid may explain why cancer that invades it becomes much more likely to spread. Draining into the lymphatic system, the newfound network is the source of lymph, the fluid vital to the functioning of immune cells that generate inflammation. Furthermore, the cells that reside in the space, and collagen bundles they line, change with age, and may contribute to the wrinkling of skin, the stiffening of limbs, and the progression of fibrotic, sclerotic, and inflammatory diseases.
The field has long known that more than half the fluid in the body resides within cells, and about a seventh inside the heart, blood vessels, lymph nodes, and lymph vessels. The remaining fluid is “interstitial,” and the current study is the first to define the interstitium as an organ in its own right, and as one of the largest of the body, say the authors.
For the original article see: Researchers Find New ‘Organ’ Missed by Gold Standard Methods for Visualizing Anatomy & Disease | NYU Langone Health
Our Model